
Data Privacy in Financial Services: Best Practices and Strategies
Data privacy is critical to financial services, ensuring that sensitive customer information remains secure from unauthorized access and cyber threats. With the increasing digitization of financial transactions, protecting data has become more challenging. Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented strict guidelines to enforce data privacy, making compliance a key focus for financial institutions. However, the evolving nature of cyber threats requires continuous advancements in security measures.
 Understanding Data Privacy in Financial Services
Understanding Data Privacy in Financial Services
Data privacy in financial services protects personal and financial information from breaches, misuse, or unauthorized access. It involves securing data throughout its lifecycle, from collection to storage and transmission. Financial institutions rely on data for business operations, fraud prevention, and customer experience improvement. Key stakeholders include financial institutions, regulators, customers, and third-party service providers. A strong data privacy framework helps maintain consumer trust, ensures legal compliance, and reduces financial risks.
 Regulatory Framework for Financial Data Privacy
Regulatory Framework for Financial Data Privacy
Data privacy in financial services is governed by a variety of regulations that ensure the protection of sensitive customer information. Compliance with these regulations is a legal requirement and essential for maintaining consumer trust and preventing financial fraud. Failure to comply with these laws can lead to significant penalties, economic losses, and reputational damage for financial institutions. Below are some of the key regulatory frameworks governing financial data privacy.
Non-compliance with these regulations can have severe consequences, including regulatory fines, legal action, and reputational harm. Financial institutions must invest in robust data security strategies, employee training programs, and continuous monitoring of data privacy practices to ensure compliance and maintain consumer confidence.
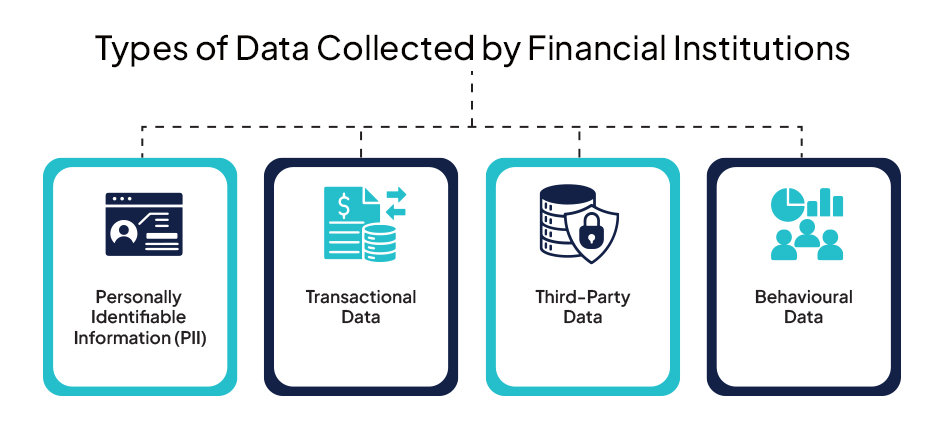
Types of Data Collected by Financial Institutions
Financial institutions collect vast data to provide services, assess risk, and detect fraudulent activities. However, handling this data comes with significant security responsibilities.
The four main types of data collected by financial institutions include:
While collecting and analyzing this data is crucial for operational efficiency, financial institutions must implement strong security protocols to prevent unauthorized access and misuse. Proper encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments are essential to safeguard sensitive customer information.
Common Data Privacy Challenges in Financial Services
Financial institutions face numerous challenges in maintaining data privacy and security. Organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in their data protection strategies as cyber threats evolve.
Below are some of the most pressing challenges in financial data privacy:
 Cyber Threats: Financial institutions are prime targets for cybercriminals who use phishing attacks, ransomware, and hacking techniques to steal sensitive customer data. Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, making it critical for financial organizations to invest in advanced cybersecurity solutions, threat detection systems, and employee training to mitigate risks.
Cyber Threats: Financial institutions are prime targets for cybercriminals who use phishing attacks, ransomware, and hacking techniques to steal sensitive customer data. Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, making it critical for financial organizations to invest in advanced cybersecurity solutions, threat detection systems, and employee training to mitigate risks.
 Insider Threats: Not all data breaches result from external attacks. Employee negligence or malicious intent can also lead to significant data leaks. Financial institutions must implement strict access controls, conduct regular security audits, and provide cybersecurity awareness training to employees to reduce the risk of insider threats.
Insider Threats: Not all data breaches result from external attacks. Employee negligence or malicious intent can also lead to significant data leaks. Financial institutions must implement strict access controls, conduct regular security audits, and provide cybersecurity awareness training to employees to reduce the risk of insider threats.
 Third-Party Risks: Many financial institutions rely on third-party vendors and service providers to handle data processing, cloud storage, and transaction services. If these third parties do not have robust security measures, they can become weak points in the data protection chain. Organizations must perform thorough security assessments of their vendors and enforce strict data privacy agreements.
Third-Party Risks: Many financial institutions rely on third-party vendors and service providers to handle data processing, cloud storage, and transaction services. If these third parties do not have robust security measures, they can become weak points in the data protection chain. Organizations must perform thorough security assessments of their vendors and enforce strict data privacy agreements.
 Regulatory Complexities: Financial institutions operating across multiple jurisdictions must comply with various international and regional data privacy laws. Navigating different compliance requirements can be challenging, and failure to meet regulatory standards can result in heavy fines and legal consequences. Institutions must stay updated on evolving data privacy laws and implement compliance frameworks to ensure adherence.
Regulatory Complexities: Financial institutions operating across multiple jurisdictions must comply with various international and regional data privacy laws. Navigating different compliance requirements can be challenging, and failure to meet regulatory standards can result in heavy fines and legal consequences. Institutions must stay updated on evolving data privacy laws and implement compliance frameworks to ensure adherence.
Real-Life Financial Data Breaches, Costs, and Regulatory Comparison
In 2017, Equifax, one of the largest credit reporting agencies in the United States, experienced a significant data breach that exposed the personal information of approximately 148 million individuals. The compromised data included names, home addresses, phone numbers, dates of birth, Social Security numbers, and driver’s license numbers. Additionally, the credit card numbers of around 209,000 consumers were also breached. This incident underscored the critical importance of robust data security measures within financial institutions.
Source: archive.epic.org
The financial repercussions of data breaches in the banking sector are substantial. As of 2024, the average cost of a data breach in the financial industry worldwide was $6.08 million, up from $5.90 million in 2023. This figure is notably higher than the global average across all industries, which stood at $4.88 million in 2024. These costs encompass various factors, including lost business, regulatory fines, and post-breach response expenses.
Source: statista.com
Key Aspects of the Regulatory Landscape
To provide a clearer understanding of the regulatory landscape, the following table compares key aspects of GDPR, CCPA, and PCI DSS:
| Aspect | GDPR | CCPA | PCI DSS |
| Scope | Applies to all organizations processing personal data of EU residents, regardless of location. | Applies to businesses that collect personal data of California residents and meet certain thresholds. | Applies to all entities involved in payment card processing, including merchants, processors, acquirers, issuers, and service providers. |
| Key Requirements | – Obtain explicit consent for data processing. – Provide data subjects with rights to access, rectify, and erase their data. – Conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs). – Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) in certain circumstances. |
– Disclose data collection practices to consumers. – Allow consumers to opt-out of the sale of their personal information. – Provide consumers with access to their data upon request. – Delete consumer data upon request, with some exceptions. |
– Maintain a secure network. – Protect cardholder data through encryption. – Implement strong access control measures. – Regularly monitor and test networks. – Maintain an information security policy. |
| Penalties for Non-Compliance | Fines up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. | Fines up to $7,500 per intentional violation and $2,500 per unintentional violation. | Penalties vary but can include fines, increased transaction fees, or revocation of the ability to process card payments. |
Understanding these regulations and implementing appropriate compliance measures are essential for financial institutions to protect consumer data and avoid significant penalties.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Privacy in Financial Services
Financial institutions must implement a comprehensive security strategy to safeguard customer data and maintain compliance with data privacy regulations.
The following best practices can help enhance data privacy in financial services:
 1. Strong Encryption Protocols: Encrypting data in transit and at rest ensures that sensitive customer information remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. Encryption protects against data breaches and enhances security across financial transactions.
1. Strong Encryption Protocols: Encrypting data in transit and at rest ensures that sensitive customer information remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. Encryption protects against data breaches and enhances security across financial transactions.
 2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using multiple authentication methods, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time verification codes. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and enhances account security.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity using multiple authentication methods, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time verification codes. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and enhances account security.
 3. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implementing RBAC ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific types of data based on their job roles. Limiting access minimizes the risk of data breaches and prevents unauthorized data handling.
3. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implementing RBAC ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific types of data based on their job roles. Limiting access minimizes the risk of data breaches and prevents unauthorized data handling.
 4. Regular Security Audits: Conducting periodic security audits helps financial institutions identify vulnerabilities, detect potential threats, and assess compliance with data privacy regulations. Regular audits allow organizations to address security gaps and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture proactively.
4. Regular Security Audits: Conducting periodic security audits helps financial institutions identify vulnerabilities, detect potential threats, and assess compliance with data privacy regulations. Regular audits allow organizations to address security gaps and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture proactively.
 5. Zero-Trust Architecture: Adopting a zero-trust model requires continuous verification of access requests, ensuring that no user or device is trusted by default. This approach helps financial institutions prevent unauthorized access, detect potential threats in real-time, and enhance overall data security.
5. Zero-Trust Architecture: Adopting a zero-trust model requires continuous verification of access requests, ensuring that no user or device is trusted by default. This approach helps financial institutions prevent unauthorized access, detect potential threats in real-time, and enhance overall data security.
By following these best practices, financial institutions can strengthen their data privacy strategies, reduce security risks, and ensure regulatory compliance. A proactive approach to data protection enhances customer trust and safeguards financial institutions from costly data breaches and cyberattacks.
Importance of Customer Awareness and Education
Customers play a crucial role in data privacy. Financial institutions must educate customers about data privacy risks and safe online practices. Transparency in data usage policies helps build customer trust and encourages responsible data sharing.
Conclusion
Data privacy in financial services is more important than ever, requiring a strategic approach involving regulatory compliance, advanced technology, and customer awareness. Financial institutions can ensure a secure financial ecosystem for their customers by implementing best practices and staying ahead of emerging threats.
FAQs
How Can Datavision help?
We assist various financial institutions and global banks on their digital transformation journey. Our one-of-a-kind approach, which combines people, process, and technology, expedites the delivery of superior results to our clients and drives excellence. Several reputed companies leverage our proprietary suite of business excellence tools and services to unlock new growth levers and unparalleled ROI.
Datavision stands proudly as a prominent banking software solutions provider, recognized for our unwavering commitment to excellence in the industry. We have earned our esteemed reputation by consistently delivering cutting-edge core banking software, catering to the needs of both retail and corporate banking software sectors. At Datavision, our mission is clear: to provide our clients with the best banking software products, ensuring that they stay ahead in an ever-evolving financial landscape. We take pride in serving our prestigious clients and look forward to continuing our journey of innovation and excellence.
Our portfolio of banking software product and services include:
Core Banking Solutions: | FinNext Core | Banking: | FinTrade | EasyLoan | MicroFin |
Digital Banking Solutions: | IBanc | MobiBanc | MBranch | FinTab | FinSight |
Risk & Compliance: |FinTrust |
Want to know how our team of experts at Datavision provides customizable, scalable, and cost-effective banking software products and solutions to our esteemed clients? Visit us for more information.