
Introduction
The global economy faces an ongoing challenge: money laundering and financial crimes that threaten the integrity of financial systems. To combat this, financial institutions, regulators, and authorities worldwide have implemented stringent Anti-Money Laundering (AML) measures. One of the pivotal tools in this battle is the Suspicious Activity Report (SAR). I In this article, we will provide an in-depth exploration of SARs and their complexities. We will cover all the essential details related to SARs, why they are crucial, and the comprehensive range of AML measures that work hand in hand with them.

Understanding Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs)
A Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) is a formal, confidential document filed by financial institutions, such as banks, money service businesses, and credit unions, to alert government authorities about transactions or activities that may raise suspicion of money laundering, fraud, or other illicit financial activities. SARs are instrumental in the fight against financial crimes as they serve as a primary channel for financial institutions to report and share suspicions with regulatory bodies.
SARs should be filed when there is a reasonable suspicion that a transaction or activity involves illicit funds or financial wrongdoing. Identifying suspicious activities can be a complex task, but it typically consists of recognizing red flags such as:
Filing a SAR is a legal obligation in many jurisdictions and can have severe consequences if ignored.
One of the most critical aspects of SARs is the confidentiality and legal protections they offer. Financial institutions and their employees are safeguarded by law when they file SARs. Whistleblower protections and confidentiality safeguards ensure that institutions and individuals can report suspicions without fear of retribution or legal consequences.
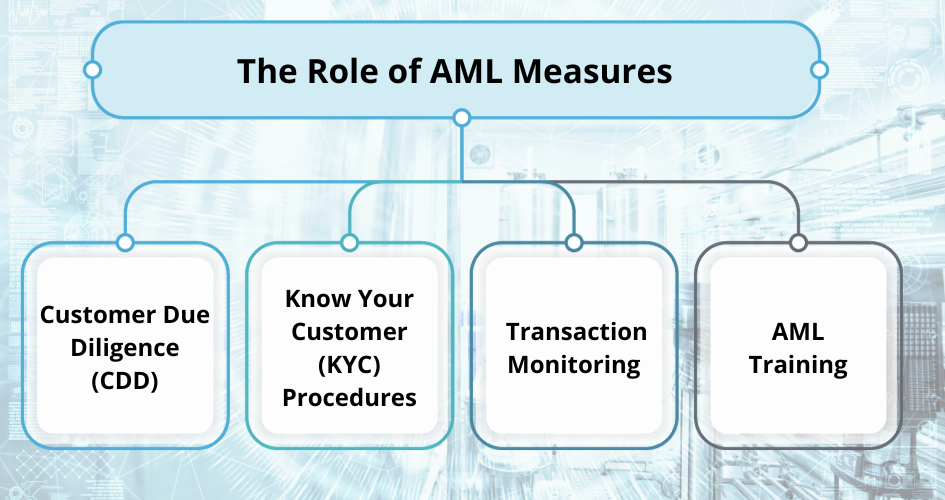
The Role of AML Measures
What is Anti-Money Laundering (AML)?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) refers to a comprehensive set of regulations, laws, and practices designed to deter, detect, and prevent the illegal generation of income and the subsequent conversion of that income into legitimate assets. AML measures are vital to the global financial system’s stability, security, and integrity.
Key AML Measures
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a fundamental AML measure that requires financial institutions to conduct a thorough background check on their customers.
The process includes:
Enhanced CDD is often applied to high-risk customers.
Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures are closely related to CDD. They involve collecting relevant information about customers to ensure their identities are genuine and match the information they provide. KYC helps institutions spot discrepancies in customer information, which could be a strong indicator of money laundering.
Transaction monitoring is a real-time or periodic review of transactions to identify unusual patterns or activities. Sophisticated AML software is employed to scrutinize transactions, making it possible to detect suspicious or unusual activities promptly. If a transaction falls outside the norm, it may trigger a review and potential SAR filing.
One of the cornerstones of effective AML is a well-trained workforce. Employees within financial institutions must be educated and trained to recognize potential red flags and report suspicious activities effectively. Regular training and ongoing education programs are crucial for keeping the workforce vigilant.
The Importance of SARs in AML
SARs are indispensable tools within the AML framework. They enable financial institutions to promptly report suspicious activities, reducing the risk of money laundering and other financial crimes. The role of SARs extends beyond the institution itself; they provide crucial information for law enforcement agencies to investigate and combat illicit financial activities.
Effective AML measures, including SARs, foster collaboration between financial institutions, government agencies, and regulatory bodies. This collaborative approach creates a comprehensive network of safeguards for more effective AML efforts. By collaborating, the global financial community thwarts criminals from exploiting the financial system.
Conclusion
In the battle against money laundering and financial crimes, Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) are invaluable instruments. They provide financial institutions with a structured means to report suspicions, thereby aiding in the prevention and detection of money laundering. When combined with robust Anti-Money Laundering (AML) measures, SARs create a comprehensive defense against illicit financial activities.
Financial professionals must understand the significance of SARs and be well-versed in AML measures to create a secure financial environment. By filing SARs and diligently implementing AML measures, we can collectively safeguard our financial systems from the pervasive threats of money laundering and other illicit financial activities. The global commitment to AML measures and the effective use of SARs is pivotal in ensuring the integrity of the global financial system.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is the purpose of a SAR?
A: The primary purpose of a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) is to enable financial institutions to report and share suspicions of money laundering, fraud, or other illicit financial activities with regulatory authorities. SARs play a crucial role in detecting and preventing financial crimes.
Q2: Can individuals file SARs, or are they exclusive to financial institutions?
A: SARs are typically filed by financial institutions and certain designated professionals, such as lawyers and accountants. Individuals may report suspicions to the institution, which can then file a SAR based on that information.
Q3: How confidential are SARs, and who has access to them?
A: SARs are highly confidential. They are shared only with relevant law enforcement and regulatory agencies responsible for combating financial crimes. Access to SARs is restricted to authorized personnel to protect the privacy of the reporting institution and individuals involved.
Q4: Are there penalties for not filing a required SAR?
A: Yes, there can be severe penalties for failing to file a required SAR. Penalties may include fines, legal actions against the institution, and even criminal charges for wilful non-compliance.
Q5: Are there international standards for SARs and AML measures?
A: While there are international organizations and initiatives aimed at promoting AML efforts and SAR-related activities, standards and regulations can vary from one jurisdiction to another. Financial institutions are generally required to follow local AML laws and regulations.
Q6: Why is Customer Due Diligence (CDD) important in AML?
A: CDD is crucial because it helps financial institutions assess the risk associated with each customer, verify their identity, and gather necessary information to prevent money laundering. It ensures that the institution knows who they are doing business with.
Q7: What is the role of AML software in transaction monitoring?
A: AML software automates the process of monitoring transactions in real-time. It can quickly identify patterns or activities that deviate from the norm and may indicate money laundering or other financial crimes.
Q8: Is AML training mandatory for all employees in financial institutions?
A: AML training is typically mandatory for all employees in financial institutions who are involved in customer interactions, transaction processing, and compliance functions. Ensuring employees are aware of AML requirements and can identify suspicious activities.
Q9: How do KYC procedures differ from CDD?
A: KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures are a subset of CDD (Customer Due Diligence). While CDD encompasses a more comprehensive assessment of customer risk, KYC focuses on verifying the customer’s identity and gathering essential information.
Q10: Do AML measures differ from one country to another?
A: Yes, AML measures can vary from one country to another, depending on local laws and regulations. However, there are international initiatives, such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), that set global standards for AML efforts.
How Can Datavision help?
We assist various financial institutions and global banks on their digital transformation journey. Our one-of-a-kind approach, which combines people, process, and technology, expedites the delivery of superior results to our clients and drives excellence. Several reputed companies leverage our proprietary suite of business excellence tools and services to unlock new growth levers and unparalleled ROI.
Datavision stands proudly as a prominent banking software solutions provider, recognized for our unwavering commitment to excellence in the industry. We have earned our esteemed reputation by consistently delivering cutting-edge core banking software, catering to the needs of both retail and corporate banking software sectors. At Datavision, our mission is clear: to provide our clients with the best banking software products, ensuring that they stay ahead in an ever-evolving financial landscape. We take pride in serving our prestigious clients and look forward to continuing our journey of innovation and excellence.
Our portfolio of banking software product and services include:
Core Banking Solutions: | FinNext Core | Banking: | FinTrade | EasyLoan | MicroFin |
Digital Banking Solutions: | IBanc | MobiBanc | MBranch | FinTab | FinSight |
Risk & Compliance: |FinTrust |
Want to know how our team of experts at Datavision provides customizable, scalable, and cost-effective banking software products and solutions to our esteemed clients? Visit us for more information.