
Financial Inclusion: Strategies for Reaching the Unbanked Population
Amidst the current digital environment, a substantial portion of the population continues to be unbanked, meaning they need to be connected to the formal banking system. The notion of digital identity arises as a crucial catalyst in tackling the existing disparity in financial inclusion. This blog explores the diverse digital identity solutions specifically designed for individuals without bank accounts. It offers insights into how these solutions can empower individuals, encouraging them to participate in the economy and helping to narrow the current financial gaps.

The Plight of Unbanked Individuals
On a worldwide level, billions of people cannot access formal banking services because of the significant challenge of identity verification. A primary obstacle faced by unbanked individuals in low-income countries is the lack of identification documentation. It is estimated that over one billion individuals worldwide, particularly in low-income economies, lack official identification documents. This staggering number underscores the urgent need for digital identity solutions to enable financial inclusion.
Unbanked individuals, often residing in remote or underserved areas, face significant challenges in accessing traditional banking services. The lack of formal identification further enhances this issue, leaving a large portion of the global population excluded from financial inclusion. However, digital identity solutions have the potential to revolutionise this landscape, transcending geographical limitations and providing access to essential banking services.
While digital identification systems are crucial in verifying an individual’s identity electronically, it’s equally important to maintain regulatory oversight to ensure their secure and efficient utilisation in the banking sector. A crucial challenge is striking a delicate balance between promoting innovation and safeguarding financial stability, integrity, and consumer protection. This requires extensive research, coordination, and collaboration with private-sector service providers to establish trust among users of digital ID solutions.
The Importance of Digital Identity in the Banking Industry
Digital identity and electronic ID verification are essential components within the banking industry, fulfilling many functions. To begin with, they streamline the procedure by which individuals lacking bank accounts can establish transaction accounts, thereby promoting the effective distribution of social benefits. Additionally, these systems cost-effectively facilitate remote enrollment by banking service providers. Furthermore, they foster the expansion of the banking industry by facilitating the adoption of supplementary products and services.
Digital identification (ID) systems provide enhanced confidence compared to manual or paper-based procedures and, in numerous scenarios, enable immediate verification of a client’s identity. Studies indicate that digital ID-enabled processes can considerably reduce customer enrollment expenses. Nevertheless, adherence to anti-money laundering and countering the funding of terrorism (AML/CFT) regulations continues to present a formidable obstacle, particularly regarding governmental cash transfer initiatives. Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations for customer due diligence (CDD) emphasise the need for formal identification documents.
FATF standards apply to conventional and digital financial services. In the financial sector, digital identification systems can improve trustworthiness, efficiency, security, and privacy when identifying individuals. Despite the expansion of digital payments, there are still restricted methods for establishing digital identification; some nations have resorted to electronic ID databases and e-KYC solutions to overcome these obstacles. In this ever-changing environment, developing digital ID systems and policies that are well-considered and foster trust and inclusion while mitigating risks and addressing technical barriers is critical.

Enabling Unbanked Individuals via Financial Inclusion
The utilisation of digital identity enables unbanked individuals to access financial services and actively engage in the economy. Financial inclusion plays a significant role in fostering economic progress by ensuring that businesses and individuals historically excluded from the formal banking system, particularly the unbanked populace devoid of fundamental financial services, have access to banking services. It is impossible to exaggerate the importance of financial inclusion, which boosts the economy, reduces poverty, and ensures social stability. Difficulties emerge due to insufficient banking infrastructure in remote regions; therefore, digital solutions such as the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) in India are indispensable for addressing this issue. UPI has significantly transformed the financial inclusion landscape by providing a secure, user-friendly, and readily available transaction platform.
However, technology cannot resolve all obstacles on its own. An all-encompassing approach encompasses cooperative endeavours to expand digital infrastructure, financial commitments to promote digital literacy, alliances to develop customised products and resilient regulatory structures. Although UPI has played a significant role, addressing areas such as dependable internet, digital literacy, and trust establishment is imperative to ensure long-term financial inclusion. In summary, it is critical to adopt a comprehensive approach to guarantee that the advantages of financial inclusion are accessible to all individuals, regardless of their geographic location or socioeconomic standing.
Outlook for the Future and Obstacles:
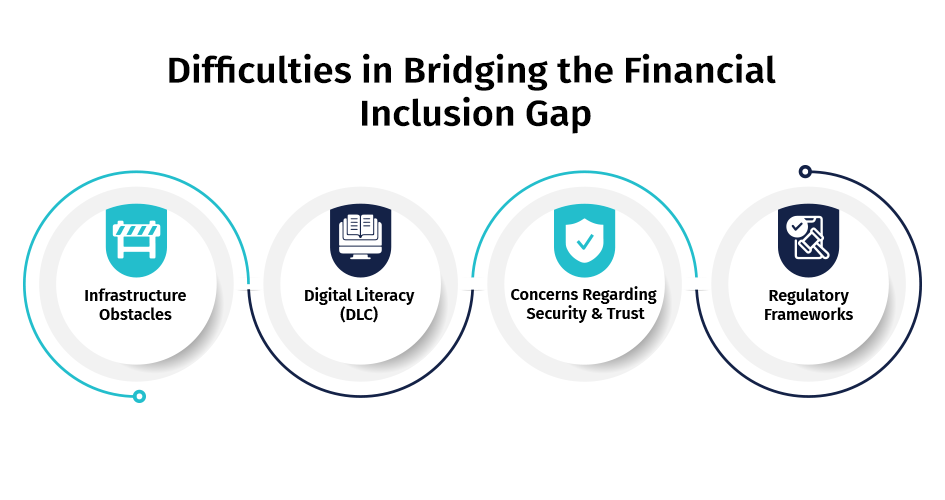
Difficulties in Bridging the Financial Inclusion Gap
Infrastructure Obstacles: In numerous geographical areas, particularly remote or underserved areas, inadequate digital infrastructure impedes the execution of resilient digital identity systems. The presence of restricted internet connectivity and technological access also presents considerable obstacles.
Digital Literacy (DLC): A significant barrier to the widespread adoption of digital identities is the considerable variation in digital literacy levels among the unbanked populace. Raising awareness and educating users regarding the advantages and secure practices associated with digital banking services is still crucial.
Concerns Regarding Security and Trust: Establishing confidence in digital identity solutions is vital. To achieve broad acceptability and implementation, it is critical to contend with apprehensions regarding data security, privacy, and the potential for digital fraud.
Regulatory Frameworks: The diversity of regulatory environments across regions hinders the development of standardised digital identity solutions. Harmonising regulations to establish universally recognised standards necessitates global coordination.
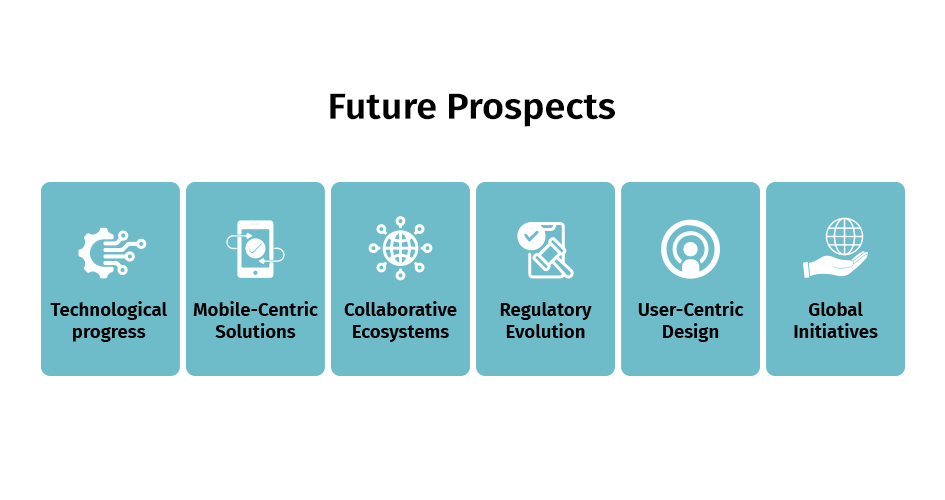
Future Prospects
Technological progress: Ongoing technological progress, such as blockchain and artificial intelligence, offers exciting prospects for improving the security and efficacy of digital identity systems, thereby enhancing their accessibility and dependability for individuals lacking bank accounts.
Mobile-Centric Solutions: Mobile-centric solutions are the future. By capitalising on the widespread availability of mobile devices, digital identity services can be provided with greater accessibility, especially in regions devoid of conventional banking infrastructure.
Collaborative Ecosystems: Partnerships formed between technology firms, governments and banking institutions will play an important role. Establishing cohesive ecosystems promotes the growth and execution of all-encompassing digital identity solutions.
Regulatory Evolution: It is critical to adopt a proactive stance toward regulatory evolution. Regulatory frameworks must continuously evolve to accommodate technological advancements while safeguarding consumer interests, promoting security, and fostering innovation.
User-Centric Design: A user-centric approach that considers the distinct requirements and obstacles faced by the unbanked can increase the acceptance and adoption of digital identity solutions, making the audience feel valued and considered in the development process.
Global Initiatives: Enhanced engagement in international initiatives that are in line with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals has the potential to galvanise enormous initiatives to provide unbanked individuals with legitimate digital identities.
Conclusion
In the ever-changing financial environment, it is critical to confront these obstacles and seize forthcoming prospects to establish digital identity as an influential instrument that can close the gap in financial inclusion and empower the unbanked population globally.
How Can Datavision help?
We assist various financial institutions and global banks on their digital transformation journey. Our one-of-a-kind approach, which combines people, process, and technology, expedites the delivery of superior results to our clients and drives excellence. Several reputed companies leverage our proprietary suite of business excellence tools and services to unlock new growth levers and unparalleled ROI.
Datavision stands proudly as a prominent banking software solutions provider, recognized for our unwavering commitment to excellence in the industry. We have earned our esteemed reputation by consistently delivering cutting-edge core banking software, catering to the needs of both retail and corporate banking software sectors. At Datavision, our mission is clear: to provide our clients with the best banking software products, ensuring that they stay ahead in an ever-evolving financial landscape. We take pride in serving our prestigious clients and look forward to continuing our journey of innovation and excellence.
Our portfolio of banking software product and services include:
Core Banking Solutions: | FinNext Core | Banking: | FinTrade | EasyLoan | MicroFin |
Digital Banking Solutions: | IBanc | MobiBanc | MBranch | FinTab | FinSight |
Risk & Compliance: |FinTrust |
Want to know how our team of experts at Datavision provides customizable, scalable, and cost-effective banking software products and solutions to our esteemed clients? Visit us for more information.