
Green Banking: Promoting Environmentally Friendly Financial Products and Practices
The banking sector plays a significant role in financing commercial projects, which are crucial for economic development. Green Banking is a concept where banks work towards restoring the natural environment and promoting environmentally friendly practices in industries. It involves promoting environmentally favourable practices and reducing the carbon footprint associated with banking activities. Sustainable banking is the responsible and thoughtful use of all bank resources, the prevention of waste, and the prioritization of sustainability decisions. As organizations strive to reduce costs, optimize operations, and establish long-term processes, green banking will enhance banks’ asset quality in the future.
This article delves into the following topics: the significance of green banking, green banking initiatives, the environmental management practices of banking institutions, enforcement of environmental management, and the role of government and green banking strategies.
Green Banking is a bank-led initiative that aims to aid the growth of green industries and, in the process, restore the natural environment. It involves integrating technology and operational enhancements and modifying client behaviours. For instance, remote deposit enables growth without physical infrastructure, ACH payments reduce outgoing mail, and e-statements conserve trees. Green Bank examines green banking from three perspectives: operational, technological, and client acceptability. They are implementing operational enhancements, including substituting daily courier services with electronic delivery and scans, electronic paychecks, and reimbursement cheques distributed to all employees.
There are various methods like Online Statements, Registration for Internet Banking for achieving environmental sustainability in the banking sector. It entails receiving monthly statements electronically, as opposed to traditional banking statements. In this manner, one contributes to reducing paper consumption and waste. Reduced costs, enhanced performance, and competitiveness are all contingent upon the implementation of an effective online banking system. The service is offered at no cost to both retail and commercial clients. Despite the economic turmoil that has caused the market to stall, numerous financial institutions and corporations emphasize sustainability.
Banks are demonstrating this through policies that emphasize green lending trends and investment strategies. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) ISO-14000 is an exhaustive set of guidelines for integrating environmental protection and pollution prevention objectives into industrial activity worldwide.
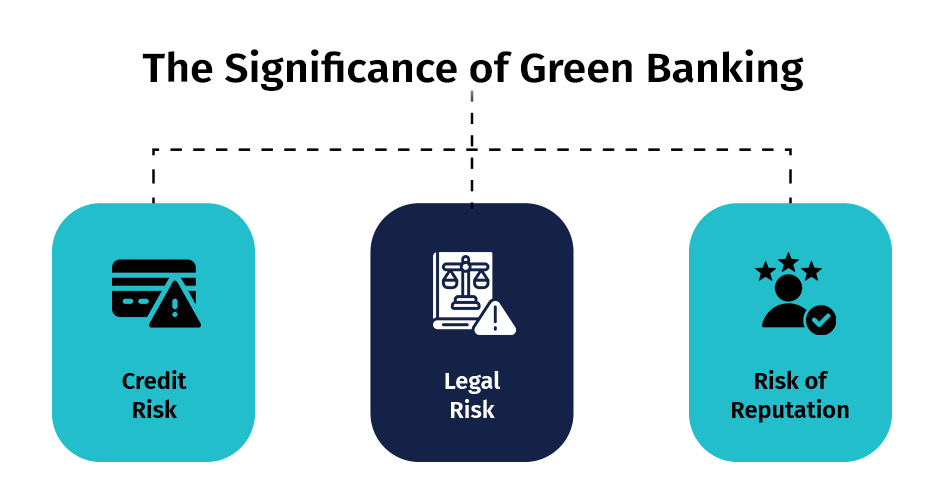
The Significance Of Green Banking
The banking sector has regarded the concern for the environmentally degrading activities of its clients as an interference in the client’s business affairs. Nevertheless, businesses are at risk when interacting with the environment. Industries would be required to adhere to specific standards to operate their businesses due to the stringent environmental regulations implemented by the competent authorities in various countries. In the event of failures, the bank would be at risk of default due to the halting of industries.
Therefore, it is crucial that financial institutions take a proactive stance in engaging with shareholders on environmental and social policy issues and assessing the impact of their client’s investments. This not only makes them more responsible but also involves them in the process of promoting green banking.
The significance of green banking is not just for the economy and banks, but also for mitigating the following risks associated with the banking sector. This emphasis on risk mitigation can make the audience feel more secure and confident in the concept of green banking.
1) Credit Risk
Credit Risk can occur when banks provide loans to consumers whose businesses are negatively impacted by the cost of pollution cleanup or changes in environmental regulations. Strict emission standards may serve as an effective strategy for eliminating specific organizations. Uncalculated expenses for investment, loss of market share, and liability claims may raise credit risks and lead to customer defaults.
2) Legal Risk
Banks and other organizations that fail to comply with pertinent environmental regulations are at risk. However, they are particularly susceptible to direct lender liability for cleanup expenses or claims damages if they have truly acquired contaminated or pollution-causing assets. Therefore, the bank can mitigate risk and expense, improve its reputation, and implement an environmental management system to capitalize on revenue opportunities.
3) Risk of Reputation
Banking institutions are increasingly at risk of losing their reputations if they participate in significant environmentally and socially detrimental projects, given the increasing awareness of environmental safety. In specific instances, implementing an environmental management system led to a reduction in risk and an increase in environmental protection, increasing operating profit and stewardship. The polluting industries face greater resistance and to cease operations or endure a significant boycott by consumers. The challenge environmental regulatory bodies face regarding the quantity and placement of polluting facilities is addressed through green banking. This risk of reputation is a significant concern for banks, as it can lead to a loss of customers and a decrease in profitability.
 Green Banking Initiatives
Green Banking Initiatives
Green Banking initiatives strive to implement measures that protect the environment, reduce pollution, and serve and finance customers. They also aim to enhance in-house environment management through the efficient and effective use of resources in all branches and head offices of banks. Commercial banks must implement the requisite safeguards to prevent environmental degradation when financing new projects or providing working capital to existing enterprises.
Banks aim to achieve the following objectives by implementing this policy:
The implementation of new technology in banking operations that would not only enhance the productivity of employees but also benefit consumers;
Financial institutions should promote initiatives that prioritize the factors during the financing process. A third-party expert, such as an environmental consultant or an independent auditor, should oversee sustainable development and the utilization of natural renewable resources, protection of human health, biodiversity, occupational health, and energy consumption, Population prevention and pollution minimization, and the development of an environmental management plan. This independent verification is crucial in ensuring that banks are adhering to their green banking policies and are not engaging in any environmentally harmful practices.
DataVision has been crafting software solutions for the Banking and Financial services industry for more than 25 years. The products developed at DataVision reflect our expertise, technology framework and thought process in delivering innovative solutions for the Banking and Financial services industry. Get in touch
 Role of Government
Role of Government
Banks, as the financing agents of the world’s economic and developmental activities, can play a crucial role in advancing sustainable development worldwide in addition to industry and agriculture. The emergence of green banking as a vital strategy for addressing sustainable development concerns and promoting environmental responsibility among the general public is a hopeful and optimistic sign, largely due to the role of the government. Green Banking involves banks prioritizing lending to industries that have already transitioned to a greener economy or are in the process of doing so, thereby contributing to restoring the natural environment.
In addition, environmental audits are necessary to ascertain the ecological status of the facility, property, and operations.
An independent body or an environmental investigative team should be established to address the project’s current issues. The government should also implement legislation to compel banks to provide a formal environmental policy statement and make it public.
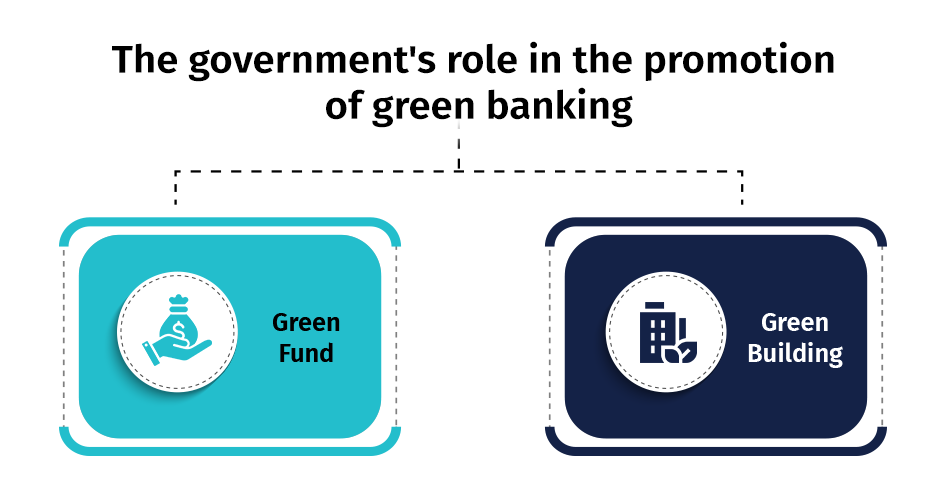
The government’s role in the promotion of green banking
Green Fund: A mutual fund that exclusively invests in companies that are socially conscious in their business operations or directly promote environmental responsibility is known as a green fund. It is a focused investment vehicle for companies involved in environmentally supportive enterprises, like alternative energy, water and waste management, green transportation, and sustainable living.
Green Buildings: The practice of green building involves developing structures and implementing processes that are resource-efficient and environmentally responsible throughout a building’s lifecycle, including design, construction, operation, maintenance and renovation.
For instance, green buildings may utilize sustainable materials in their construction (e.g., recycled, reused, or renewable resources); establish healthy indoor environments with minimal pollutants and incorporate landscaping that minimizes water consumption (e.g., by utilizing native plants that require minimal watering).
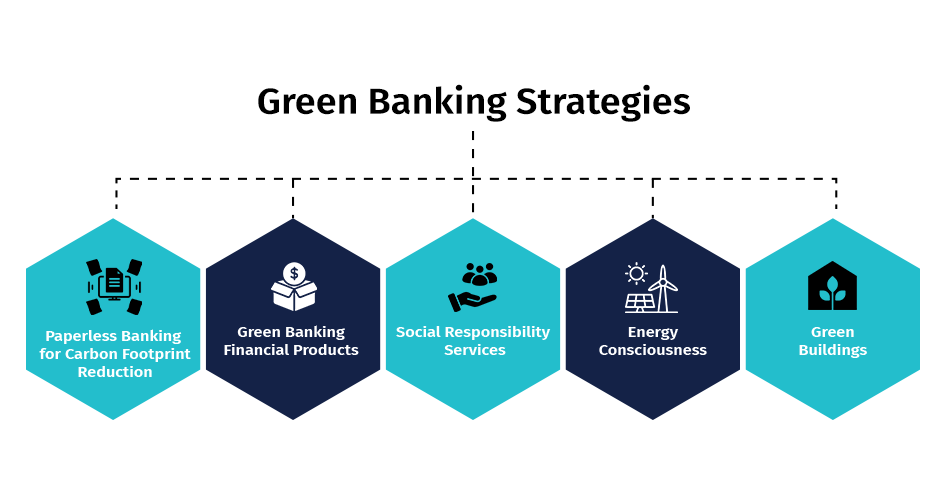
Green Banking Strategies
Banks can incorporate the following strategies to adopt green banking as a sustainable business model.
1. Paperless Banking for Carbon Footprint Reduction: The carbon footprint is a metric that quantifies the amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs). Most institutions are either computerized or operate on a core banking solution (CBS). Consequently, institutions have a significant opportunity to transition to paperless or paperless banking. These financial institutions have the option to transition to electronic correspondence.
2. Green Banking Financial Products: To offer carbon-conscious consumers the opportunity to invest in environmentally friendly initiatives, banks must implement “Green Funds.” Banks may also implement green bank loans, which offer financial incentives for environmentally friendly products and initiatives, including fuel-efficient vehicles and green infrastructure building projects, as well as housing and house furnishing loans to implement solar energy systems.
3. Social Responsibility Services: Banks have the option to implement a variety of social responsibility initiatives as part of their green banking strategy, including tree plantation camps, park maintenance, and pollution inspection camps, are provided.
4. Energy Consciousness: Developing energy consciousness through effective office time management and automation, as well as using LED lights, has the potential to significantly reduce institutions’ energy consumption. Additionally, they can transition to renewable energy sources (such as solar and wind) to operate their ATMs and offices.
5. Green Buildings: It is recommended that these institutions develop and utilize green buildings for their offices and employee accommodations. A green building is healthier for the occupants, generates less waste, and is less energy, water, and natural resource-intensive than a standard building.
These measures will not only assist banks in reducing their carbon footprint but also significantly reduce their operational costs.
Conclusion
Banks, similar to their corporate clients, have recognized that sustainability and profitability are interlinked as organizations strive to reduce expenses, optimize operations, and establish sustainable processes. If implemented with integrity, the green banking system will serve as an active deterrent for the polluting industry that bypasses the other institutional regulatory mechanism. The banks and other financial institutions have yet to take much initiative in this regard despite their influential role in the economy. The financial industry and the banking sector should be encouraged to contribute to sustainable development in the context of green banking. As consumers increasingly doubt the long-term sustainability of fossil fuels as an energy source, green banks are emerging as viable alternatives to conventional banks. Green banking institutions will undoubtedly continue to rise in the decades ahead.
How Can Datavision help?
We assist various financial institutions and global banks on their digital transformation journey. Our one-of-a-kind approach, which combines people, process, and technology, expedites the delivery of superior results to our clients and drives excellence. Several reputed companies leverage our proprietary suite of business excellence tools and services to unlock new growth levers and unparalleled ROI.
Datavision stands proudly as a prominent banking software solutions provider, recognized for our unwavering commitment to excellence in the industry. We have earned our esteemed reputation by consistently delivering cutting-edge core banking software, catering to the needs of both retail and corporate banking software sectors. At Datavision, our mission is clear: to provide our clients with the best banking software products, ensuring that they stay ahead in an ever-evolving financial landscape. We take pride in serving our prestigious clients and look forward to continuing our journey of innovation and excellence.
Our portfolio of banking software product and services include:
Core Banking Solutions: | FinNext Core | Banking: | FinTrade | EasyLoan | MicroFin |
Digital Banking Solutions: | IBanc | MobiBanc | MBranch | FinTab | FinSight |
Risk & Compliance: |FinTrust |
Want to know how our team of experts at Datavision provides customizable, scalable, and cost-effective banking software products and solutions to our esteemed clients? Visit us for more information.