
Top Challenges in Developing Secure Fintech Applications
Fintech has transformed the financial landscape, providing innovative ways to handle money, make payments, and invest. However, with this innovation comes an ever-growing need for security. Fintech applications handle sensitive financial data, making them prime targets for cybercriminals. The stakes are high: one breach can lead to severe financial loss, legal troubles, and irreparable damage to trust. This article dives deep into the top challenges of developing secure fintech applications and offers solutions to mitigate these risks effectively, highlighting the urgency of the issue.
Why Security is Crucial in Fintech Applications?
Handling Highly Sensitive Financial Data
 Personal Identifiable Information (PII)
Personal Identifiable Information (PII)
Fintech apps collect and process PII such as names, phone numbers, addresses, and identification details like Social Security or Aadhaar numbers. This data is invaluable to hackers, as it can be used for identity theft, unauthorized transactions, or creating fake accounts. Protecting this data is non-negotiable for fintech companies.
 Payment Details and Transaction Histories
Payment Details and Transaction Histories
Transaction data, including card details and payment histories, are even more sensitive. Exposure to such information can lead to fraudulent transactions and significant financial losses for both users and institutions. Secure handling of this data is critical to preserving the app’s reputation.
Maintaining Consumer Trust
 Consequences of Breaches
Consequences of Breaches
A single security breach can shatter consumer confidence. News of a data leak travels fast, damaging the credibility of even the most established fintech companies. As a developer, your role in maintaining this trust is crucial. Users may abandon the app, and new customers may steer clear, underlining the weight of your responsibility in this regard.
 Building Long-Term User Confidence
Building Long-Term User Confidence
The foundation of fintech lies in trust. When users are confident that their data and money are safe, they’re more likely to engage actively with the platform. Secure systems build this trust over time, resulting in loyal users and positive brand perception. This enhances the user experience and contributes to the long-term success and sustainability of the fintech business.
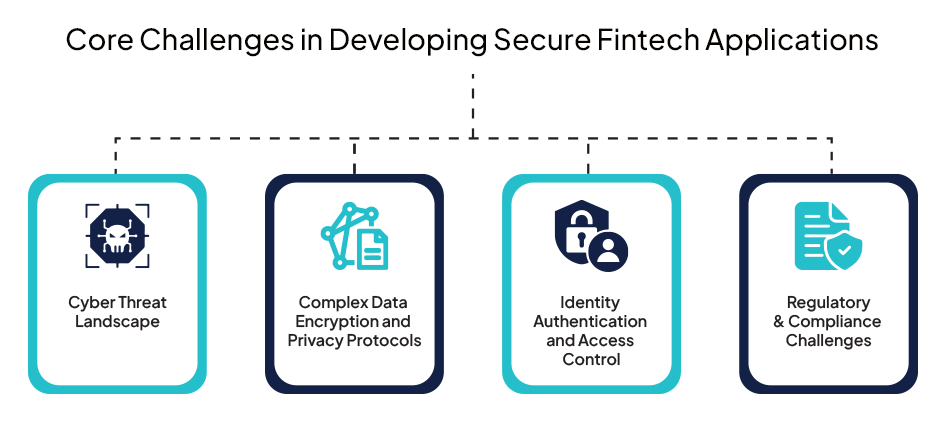
Core Challenges in Developing Secure Fintech Applications
1. Cyber Threat Landscape
2. Complex Data Encryption and Privacy Protocols
3. Identity Authentication and Access Control
4. Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Regional Compliance Complexities
Risks Introduced by Emerging Technologies
1. Vulnerabilities in AI and Machine Learning Systems
 Exploitation of ML Algorithms
Exploitation of ML Algorithms
Hackers can manipulate AI systems by introducing biased or malicious data, leading to incorrect decisions or security breaches. For instance, a compromised fraud detection algorithm might allow suspicious transactions to go unnoticed.
 Challenges in Data Integrity Management
Challenges in Data Integrity Management
AI systems rely on massive datasets to function effectively. Ensuring the accuracy and integrity of these datasets is crucial to maintaining security and reliability.
2. Blockchain Security Gaps
 Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with predefined conditions. Errors in the code can be exploited, leading to financial losses or unintended outcomes.
 Risks of Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Risks of Decentralized Applications (DApps)
While DApps offer transparency, they lack centralized oversight, making them vulnerable to targeted attacks. Developers must incorporate robust security measures without compromising the decentralized ethos.
3. Financial Constraints in Security Implementation
 Budgeting for Comprehensive Security
Budgeting for Comprehensive Security
Advanced security tools and practices come at a cost. Small and mid-sized fintech firms often face tight budgets, forcing them to prioritize certain security aspects while delaying others—a risky trade-off.
 Training and Retaining Skilled Cybersecurity Professionals
Training and Retaining Skilled Cybersecurity Professionals
Cybersecurity experts are in high demand, and retaining talent can be challenging. Companies must invest in competitive salaries and ongoing training to ensure their teams are equipped to handle emerging threats.
4. Proactive Solutions to Fintech Security Challenges
 Layered Security Architectures
Layered Security Architectures
A multi-layered approach ensures that others can protect the system if one layer is breached. This includes combining firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption.
 Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Biometric Security
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Biometric Security
Multi-factor authentication adds additional security layers by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple means, such as passwords and biometric scans. This significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access.
 Ongoing Risk Assessment and Penetration Testing
Ongoing Risk Assessment and Penetration Testing
Regularly testing systems for vulnerabilities helps identify potential weaknesses before attackers exploit them. It’s a proactive approach to maintaining a secure environment.
 Customer Awareness Campaigns
Customer Awareness Campaigns
Educating users about safe online practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts and using strong passwords, reduces the risk of human error—a shared vulnerability.
5. Emerging Trends in Fintech Security
 Rise of Zero-Trust Security Frameworks
Rise of Zero-Trust Security Frameworks
Zero-trust frameworks operate on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” They require strict authentication and continuously monitor user activity, ensuring heightened security.
 Biometric Authentication Enhancements
Biometric Authentication Enhancements
Innovations in biometric technology, like voice recognition and vein mapping, offer enhanced accuracy and security, making it harder for attackers to bypass authentication systems.
 Secure Integration of AI
Secure Integration of AI
AI-driven security measures, such as real-time fraud detection and behavioral analysis, are becoming indispensable. However, developers must ensure these systems are protected against manipulation.
Conclusion
Securing fintech applications is challenging. It requires a multifaceted approach to combat cyber threats, comply with evolving regulations, and adopt emerging technologies. While the challenges are significant, proactive measures and continuous vigilance can help fintech companies build trust, enhance user experience, and protect sensitive financial data in an increasingly digital world.
FAQs
How Can Datavision help?
We assist various financial institutions and global banks on their digital transformation journey. Our one-of-a-kind approach, which combines people, process, and technology, expedites the delivery of superior results to our clients and drives excellence. Several reputed companies leverage our proprietary suite of business excellence tools and services to unlock new growth levers and unparalleled ROI.
Datavision stands proudly as a prominent banking software solutions provider, recognized for our unwavering commitment to excellence in the industry. We have earned our esteemed reputation by consistently delivering cutting-edge core banking software, catering to the needs of both retail and corporate banking software sectors. At Datavision, our mission is clear: to provide our clients with the best banking software products, ensuring that they stay ahead in an ever-evolving financial landscape. We take pride in serving our prestigious clients and look forward to continuing our journey of innovation and excellence.
Our portfolio of banking software product and services include:
Core Banking Solutions: | FinNext Core | Banking: | FinTrade | EasyLoan | MicroFin |
Digital Banking Solutions: | IBanc | MobiBanc | MBranch | FinTab | FinSight |
Risk & Compliance: |FinTrust |
Want to know how our team of experts at Datavision provides customizable, scalable, and cost-effective banking software products and solutions to our esteemed clients? Visit us for more information.